A Clear Breakdown for Product Teams, Hardware Engineers, and Innovators
Modern smartphones rely on highly engineered display modules built from multiple optical, electrical, and structural layers. Understanding these internal components is essential for teams working on product development, manufacturability, and long-term reliability.
At class 10,000 cleanroom levels, even a microscopic dust particle can cause visible defects—such as light leakage, mura, or dead pixels. This is why display assembly is performed under strict environmental controls. Below is an engineering-focused breakdown of a standard display module combining Touch Panel (TP) and LCD.
⸻
Key Components of a Smartphone Display Module
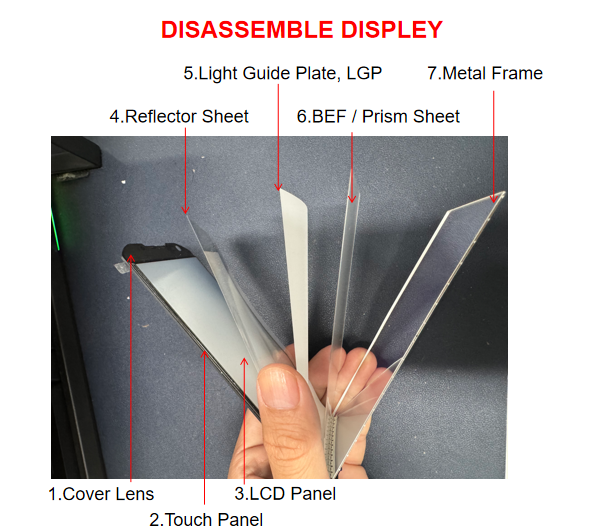
- Cover Lens (Glass)
The topmost layer users touch daily.
• Provides rigidity, scratch resistance, and impact protection
• Supports chemical strengthening (e.g., ion exchange)
• Customizable for radius, thickness, coating, and logo printing
⸻
- Touch Panel (TP)
A transparent sensor stack that detects finger input.
• Usually OGS or TOL designs
• IC bonding via COF/FOG
• Sensitive to bonding pressure, humidity, and ESD control during assembly
⸻
- LCD Panel
The primary visual layer where pixels form images.
• Includes TFT array, liquid crystal, color filter
• Requires precise alignment and uniform backlight illumination
• Manufacturing defects commonly include mura, light leakage, and pixel abnormalities
⸻
- Reflector Sheet
Reflects unused light back toward the user.
• Improves brightness and reduces power consumption
• Material selection affects heat distribution and display uniformity
⸻
- Light Guide Plate (LGP)
Distributes backlight evenly across the display.
• PMMA or polycarbonate materials
• Micro-dot pattern is laser or photo-etched
• Optical design directly affects uniformity and edge brightness
⸻
- Prism Sheet (BEF)
Brightness Enhancement Film.
• Compresses light into a forward direction
• Typically laminated in multiple layers for more efficiency
• Sensitive to scratches, static, and dust intrusion
⸻
- Metal Frame (Bracket/Bezel)
The supporting mechanical structure.
• Maintains the dimensional stability of the module
• Ensures alignment for all optical layers
• Critical for drop performance and internal space management
⸻
Why This Matters for Product Development
A display module’s design and assembly process impact:
• Touch accuracy
• Color consistency & brightness uniformity
• Battery consumption
• Drop performance
• Yield and production stability
Understanding these components helps product teams make better decisions when balancing performance, cost, manufacturability, and reliability.
At DUMU, we assist clients from concept design, mechanical engineering, prototype validation, to small-batch manufacturing—ensuring every structural detail, including display integration, is optimized for real-world production.